Welcome to the GEOS 420, Earth System Modeling, webpage for the Spring 2022 semester.
I will try to update this page every few days during the semester.
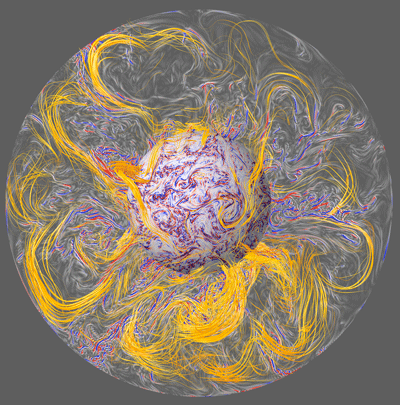
How does the Earth's core effect life on Earth? Above: Earth’s core as modelled in the numerical geodynamo simulation. More here.
Spring 2022 Lectures on Zoom: MWF, 10:00 - 10:50 AM.
Required book: The Earth System, 3rd Edition by Kump et al.
Mon. 24 Jan., Review syllabus and begin Chapter 14: Pleistocene Glaciation. Foraminifera and isotopes.
Weds., 26 Jan., Glacials and interglacials from sediment and ice cores. Evidence of glaciers and ice sheets.
Fri., 28 Jan., Temperature proxy and CO2 from ice cores. Earth orbital variations (Milankovitch theory).
Mon., 31 Jan., Faint Young Sun paradox, KT boundary and meteor impacts, begin volcanic eruptions.
Weds., 2 Feb., complete impacts of volcanic eruptions on climate. Discuss holocene, sunspot cycle.
Fri., 4 Feb., Begin Chapter 2: Daisyworld (An Introduction to Systems.)
Mon., 7 Feb., Conclude Chapter 2. Daisyworld's response to increasing solar luminosity. Feedbacks.
Weds., 9 Feb., Begin Chapter 3: Global Energy Balance. EM radiation, inverse square law, blackbody radiation.
Fri., 11 Feb., Derive energy balance equation for planet with no atmosphere. Effective radiating temperature.
Mon., 14 Feb., Quiz #1. 1-layer atmosphere and greenhouse effect. Then discussion of "models" and radiative properties of various substances.
Weds., 16 Feb., Composition of the atmosphere, selection absorption of radiation by greenhouse gases.
Fri., 18 Feb., Vertical structure of the atmosphere: derivation of the hydrostatic equation and barometric law.
Mon., 21 Feb., Absorption lines, Bouguer's law, global energy budget, global warming.
Weds., 23 Feb., Review of weather versus climate. Global vs regional climate, radiative forcing.
Fri., 25 Feb., The effects of clouds on climate. Describe parameterizations and 1D radiative-convective model.
Mon., 28 Feb., General circulation models, pattern predictability versus statistical results from pattern forecasts.
Weds., 2 Mar., Discussion of how to do Special Assignment #1.
Fri., 4 Mar., Exam #1 (100 points) on everything covered so far.
Mon., 7 Mar., Begin Chapter 4: Atmospheric circulation. Derivation of ideal gas law, and discussion of convection.
Weds., 9 Mar., Derive dry adiabatic lapse rate. How vertical movement of air leads to changes in parcel T (adiabatic process).
Fri., 11 Mar., Revisit barometric law: how changes in T lead to horizontal PGFs, wind, Coriolis effect, and geostrophic flow.
Mon., 14 Mar., Spring break. No classes.
Weds., 16 Mar., Spring break. No classes.
Fri., 18 Mar., Spring break. No classes.
Mon., 21 Mar., All students installed Matlab and took first steps using Matlab: creating variables and doing simple math.
Weds., 23 Mar., Continued learning how to use Matlab: writing a script, for loop, and if-then-else structures.
Fri., 25 Mar., What is a flowchart? How to do Question #2 in Special Assignment #1 in Matlab.
Mon., 28 Mar., The atmospheric boundary layer and the effect of turbulence in disrupting geostrophic balance.
Weds., 30 Mar., The global atmospheric circulation: 3-cell model, tropical, mid-latitude, and polar weather and climate.
Fri., 1 Apr., More assistance with Special Assignment 01 in Matlab.
Mon., 4 Apr., The stratosphere: the annual cycle at high latitudes, SSWs, Brewer-Dobson, ozone hole, and the QBO.
Weds., 6 Apr., The global hydrologic cycle with emphasis on regional surface evaporation and precipitation.
Fri., 8 Apr., Large quiz (40 points) on Chapter 4. (No lecture.)
Mon., 11 Apr., Begin Chapter 5 on the Circulation of the Oceans. Overview of the oceans.
Weds., 13 Apr., Vagn Ekman and the Ekman spiral, Ekman transport, Ekman pumping, major gyres.
Fri., 15 Apr., Eastern and western boundary currents, conservation of absolute vorticity, and asymmetry of the major gyres.
Mon., 18 Apr., Meridional versus zonal cross-sections. Walker cells and the Western Pacific warm pool.
Weds., 20 Apr., El Nino and the Southern Oscillation, La Nina, and regional and global impacts.
Fri., 22 Apr., Salinity, processes that add and remove salt, sea water density, equations of state for sea water.
Mon., 25 Apr., Formation of bottom water at high latitudes, AMOC, Sandström's theorem, heat engines, and heat pumps.
Weds., 27 Apr., The global ocean as a heat pump. Excerpts from Rui Xin Huang's Ocean Circulation
Fri., 29 Apr., Begin Chapter 6: The Cryosphere. Reasons of importance, cryospheric components. Begin ice sheets and Greenland.
Mon., 2 May, Exam/Quiz on Chapter 5 (Oceans)
Weds., 4 May, Discussion of expectations for homework. Then, continue with Antarctica and ice flows, ice streams, ice shelves
Fri., 6 May, Snow, Bergeron process, compaction of snow in glaciers, permafrost, methane, begin sea ice.
Mon., 9 May, Review week
Weds., 11 May, Review week
Fri., 13 May, Review week
Weds., 18 May, Final comprehensive exam
Dr. Mayor's page
